IGNOU offers a foundational course called BCS-11, or Computer Basics and PC Software, which introduces students to the basic ideas of computers and frequently used PC software. The goal of this course is to give students a thorough understanding of the fundamentals of computers, including principles related to networking, operating systems, software, and hardware. BCS-11 gives students the fundamental knowledge and abilities needed to navigate and use computers in a variety of personal and professional contexts through a combination of academic instruction and hands-on practice. Students should be able to use common PC software programs for communication and productivity by the end of the course, as well as have a solid understanding of computer basics.

Introduction Of BCS-11
The Computer Basics and PC Software course, or BCS-11, is a fundamental first step into the field of computers. Nowadays, with technology influencing every part of our life, it’s critical to grasp the fundamentals of computers and software. The goal of this course is to give students the fundamental knowledge they need to confidently navigate the digital world. In order to enable students use technology for both personal and professional purposes, BCS-11 covers a broad range of topics, from comprehending hardware components to investigating widely used software programs. BCS-11 provides a simple and thorough introduction to the fundamentals of computers and PC software, regardless of your level of experience.
Understanding the Importance of BCS-11 Short Notes:
1. Overview : Brief notes reduce an extensive amount of material into essential ideas and points. They offer a rapid and effective means of studying the key subjects in advance of the examination.
2. Focus on the Essentials: You may focus on each topic’s key elements by summarizing the available information. This guarantees that you cover the most relevant subjects and helps in setting priorities for your study materials.
3. Improved Retention: Taking quick notes requires you to take an active role with the information. Compared to passive reading, active learning promotes improved understanding and retention of knowledge.
4. Quick Reference: Brief notes are a quick reference that come in helpful when making last-minute changes. To fast brush up on specific concepts or formulas, you can swiftly scan them.
5. Time management: You may cover a lot of ground in less time by taking brief notes. This is very helpful if you don’t have much time to study before the test.
Most Repeated BCS-11 Important Questions for IGNOU BCA Exams Semester Wise :
Block 1 of BCS-11
Q1. Explain the Von Neumann’s architecture with the help of a diagram ?
Ans-Von Neumann architecture, proposed by Hungarian-American mathematician and physicist John von Neumann in the 1940s, is the foundational design of most modern computers. It consists of four main components: the CPU (Central Processing Unit), memory, input/output devices, and a control unit.
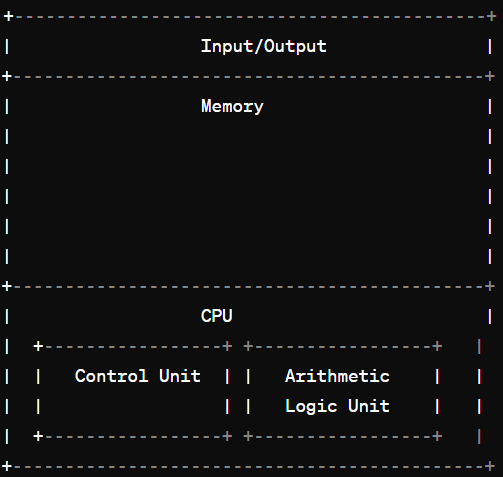
- Input/Output (I/O): This component deals with the communication between the computer and the external world. It includes devices such as keyboards, mice, monitors, printers, etc.
- Memory: This is where data and instructions are stored temporarily while the computer is running. Memory is divided into two main types: RAM (Random Access Memory) for temporary storage and ROM (Read-Only Memory) for permanent storage of essential system instructions.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the brain of the computer. It carries out instructions, performs calculations, and manages the flow of data through the system.
- Control Unit: Responsible for coordinating and controlling the activities of all other hardware components. It fetches instructions from memory, decodes them, and then executes them.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs arithmetic and logical operations, such as addition, subtraction, AND, OR, etc.
Q2. Explain the concept of memory hierarchy with the help of a diagram ?
Ans-The memory hierarchy is a structure that organizes computer memory in a hierarchy of levels, each with different characteristics regarding speed, cost, and capacity. The primary goal of the memory hierarchy is to provide the CPU with the fastest access to the most frequently used data and instructions while also optimizing cost and storage capacity. Here’s a simplified diagram illustrating the memory hierarchy:
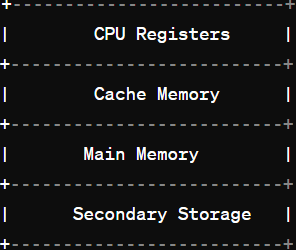
- CPU Registers: Registers are small, high-speed storage locations within the CPU itself. They hold data and instructions that are currently being processed by the CPU. Registers have the fastest access time but are limited in capacity due to their proximity to the CPU.
- Cache Memory: Cache memory is a smaller, faster type of volatile computer memory that provides high-speed data storage and access to frequently used data and instructions. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and main memory, reducing the time taken to access data and instructions that are repeatedly used.
- Main Memory (RAM): Main memory, typically referred to as RAM (Random Access Memory), is the primary volatile memory used by the computer to store data and instructions that are actively being used or manipulated by the CPU. It is larger in capacity than cache memory but slower in access speed.
- Secondary Storage: Secondary storage devices, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs), provide non-volatile storage for data and programs that are not actively being used by the CPU. Secondary storage has the largest capacity and is the slowest in terms of access speed compared to other levels of the memory hierarchy.
Q3. List the features of Generations Computer ?
Ans-
First Generation (1940s-1950s):
- Relied on vacuum tubes for circuitry.
- Used machine language for programming.
- Very large and bulky in size.
- Generated a lot of heat and were unreliable.
- Examples include ENIAC and UNIVAC.
Second Generation (1950s-1960s):
- Used transistors instead of vacuum tubes, which made them smaller, faster, and more reliable.
- Assembly language was used for programming.
- Magnetic core memory was introduced.
- Batch processing and operating systems were developed.
- Examples include IBM 1401 and IBM 7090.
Third Generation (1960s-1970s):
- Integrated Circuits (ICs) were introduced, leading to smaller, cheaper, and more powerful computers.
- High-level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN were developed, making programming easier.
- Time-sharing and multiprogramming operating systems were introduced.
- Remote data processing and networking started to emerge.
- Examples include IBM System/360 and DEC PDP-11.
Fourth Generation (1970s-present):
- Microprocessors were developed, allowing the integration of entire CPU on a single chip.
- Personal computers (PCs) became widespread, leading to a significant increase in computing accessibility.
- Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) and networking became standard.
- More advanced programming languages like C, C++, and Java were developed.
- Laptops, smartphones, and tablets became common.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies emerged.
- Examples include IBM PC, Apple Macintosh, and modern smartphones.
Fifth Generation (present and beyond):
- Focus on AI, ML, natural language processing, and robotics.
- Emphasis on parallel processing and distributed computing.
- Quantum computing research and development.
- Continued miniaturization and increase in computational power.
- Integration of computing into everyday objects (Internet of Things).
- Examples include quantum computers and AI-powered virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa.
Q4. What is a Port ?
Ans-In computing, a port refers to a specific communication endpoint or interface through which different processes or devices can communicate with each other. It can be either a physical or virtual connection point on a computer or network device.
Q5. What is a main memory ?
Ans- Main memory, also known as primary memory or RAM (Random Access Memory), is a crucial component of a computer system. It is a volatile form of memory, meaning that it loses its stored data when the computer is powered off.
Q6. Parallel port and Serial Port ?
Ans-Parallel Port:
- Definition: A parallel port is a type of interface that transfers data in parallel, meaning multiple bits of data are sent simultaneously over multiple lines.
- Usage: It was commonly used to connect printers, scanners, and external storage devices to computers, especially in older systems.
Serial Port:
- Definition: A serial port is an interface that transfers data sequentially, one bit at a time, over a single communication line.
- Usage: Serial ports were commonly used for connecting devices such as modems, mice, keyboards, and older peripherals to computers.
Q7. What is an integrated circuit ? Is microprocessor an integrated circuit ?
Ans-An integrated circuit (IC) is a small electronic circuit made up of interconnected components on a single semiconductor chip. A microprocessor is a type of integrated circuit that serves as the central processing unit (CPU) in computers and digital devices, containing millions to billions of transistors and other components on a single chip.
Block 2 of BCS-11
Q1. What is an Open source Software ?
Ans-Open-source software (OSS) refers to computer software with its source code made available and licensed with a license that allows users to study, modify, and distribute the software to anyone for any purpose. This means that the source code, the underlying instructions that make the software function, is openly accessible and can be modified and improved by users and developers. Examples of open-source software include the Linux operating system, the Firefox web browser, and the Apache web server.
Q2. What is an Operating System? List and explain any four service/functions of an operating system ?
Ans-An operating system (OS) is software that manages computer hardware and provides services for computer programs. It acts as an intermediary between applications and the computer hardware, facilitating communication and providing a platform for software execution.
Four key services/functions of an operating system are:
- Process Management:
- The OS manages processes, which are instances of executing programs. It allocates system resources (such as CPU time, memory, and I/O devices) to processes, schedules their execution, and facilitates communication and synchronization between processes.
- Memory Management:
- This involves managing the computer’s memory (RAM) to ensure efficient and optimal utilization. The OS allocates memory to processes, keeps track of memory usage, and performs tasks such as memory allocation, deallocation, and swapping to and from secondary storage (such as a hard disk).
- File System Management:
- The OS provides a file system that organizes and manages files stored on storage devices (such as hard disks, solid-state drives, and optical disks). It handles tasks such as file creation, deletion, reading, and writing, as well as managing directories and maintaining file security and permissions.
- Device Management:
- This involves managing input/output (I/O) devices such as keyboards, mice, monitors, printers, and network interfaces. The OS provides services for device detection, configuration, and control, as well as handling device interrupts and facilitating communication between devices and software applications.
Q3, What is spreadsheet ?
Ans-A spreadsheet is a computer application used for organizing, analyzing, and presenting data in tabular form. It consists of rows and columns where users can input numbers, text, formulas, and functions to perform calculations, manipulate data, and create visual representations such as charts and graphs. Spreadsheets are commonly used for tasks such as budgeting, financial analysis, project management, data entry, and creating reports. Popular spreadsheet applications include Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and LibreOffice Calc.
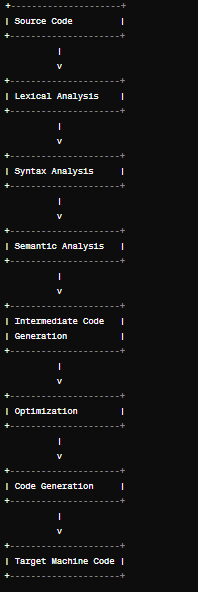
Q4. What is a Compiler ? Draw a diagram showing the different stages of the program ?
Ans-A compiler is a software tool that translates source code written in a high-level programming language into machine code or an intermediate code that can be directly executed by a computer’s hardware or by another program called an interpreter.
Q5. Memory Management in an Operating System ?
Ans-
Memory management in an operating system involves efficiently allocating and protecting memory resources for processes. Key aspects include:
- Allocation: Assigning memory space to processes dynamically or statically.
- Protection: Preventing unauthorized access to memory areas.
- Mapping: Mapping logical addresses to physical addresses for process access.
- Paging and Swapping: Managing memory by dividing it into pages and swapping pages between main memory and secondary storage.
- Cleanup and Garbage Collection: Reclaiming memory from terminated processes and unused objects to prevent memory leaks.
Q6. Compare Word Processing and Spreadsheet software ?
Ans-
Word processing and spreadsheet software are two types of applications commonly used for different purposes, yet they share some similarities. Here’s a comparison between the two:
- Purpose:
- Word Processing: Primarily used for creating, editing, formatting, and printing text-based documents such as letters, reports, essays, and memos.
- Spreadsheet: Primarily used for organizing, analyzing, and manipulating numerical and textual data in tabular form, performing calculations, and creating visual representations such as charts and graphs.
- Data Representation:
- Word Processing: Focuses on representing textual content. Documents are typically organized into paragraphs, headings, and sections.
- Spreadsheet: Focuses on representing data in tabular form with rows and columns. Each cell in the spreadsheet can contain text, numbers, formulas, or functions.
- Functionality:
- Word Processing: Offers features for formatting text (e.g., font styles, sizes, colors), adjusting page layout (e.g., margins, orientation), inserting images and multimedia, creating tables, and spell checking.
- Spreadsheet: Offers features for performing calculations using formulas and functions, sorting and filtering data, creating charts and graphs, conducting data analysis (e.g., pivot tables), and sharing and collaborating on data.
Q7. What is the role of compiler in a computer system ?
Ans-The compiler translates high-level programming language code into machine code or an intermediate representation. It optimizes code, detects errors, and generates executable programs for the computer’s hardware.
Q8. What is cloud computing ? Discuss key features of cloud computing ?
Ans-
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, providing access to a shared pool of resources including computing power, storage, and applications. Rather than owning and maintaining physical hardware and software infrastructure, users can access computing resources on-demand from cloud service providers.
Key features of cloud computing include:
- On-Demand Self-Service: Users can provision computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and applications, as needed without requiring human intervention from the service provider.
- Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible over the internet from a variety of devices including desktops, laptops, smartphones, and tablets, enabling ubiquitous access to resources from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Resource Pooling: Cloud providers aggregate computing resources from multiple physical and virtualized hardware components into a shared pool, allowing resources to be dynamically allocated and reallocated to multiple users as needed.
- Rapid Elasticity: Cloud services can scale up or down rapidly to accommodate changes in demand. Users can quickly scale their computing resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, to handle spikes in workload without significant manual intervention.
- Measured Service: Cloud computing resources are metered and billed based on usage, allowing users to pay only for the resources they consume. This pay-as-you-go pricing model enables cost-effective resource utilization and scalability.
- Resource Virtualization: Cloud computing relies on virtualization technologies to abstract physical hardware resources and present them as virtualized instances to users. This allows for greater flexibility, efficiency, and resource utilization.
- Service Models: Cloud computing offers different service models, including:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing infrastructure, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking resources, on-demand.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications without the complexity of underlying infrastructure management.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, and update software locally.
- Scalability and Reliability: Cloud computing platforms are designed to be highly scalable and reliable, with built-in redundancy, failover mechanisms, and data replication to ensure uninterrupted service availability and data integrity.
Q9. What is application software ? How is application software different from system software ?
Ans-
Application software refers to programs and applications designed to perform specific tasks or provide functionality for end-users. Unlike system software, which manages and controls computer hardware and provides a platform for running applications, application software is designed to meet the needs of users in various domains such as business, education, entertainment, communication, and productivity.
Here are some key differences between application software and system software:
- Purpose:
- Application Software: Designed to fulfill specific user needs or tasks, such as word processing, spreadsheet analysis, graphic design, web browsing, gaming, and communication.
- System Software: Designed to manage and control computer hardware and provide essential services for running applications. It includes operating systems, device drivers, utility programs, and software development tools.
- User Interaction:
- Application Software: Interacts directly with end-users, providing interfaces and tools for performing specific tasks or functions. Users interact with application software to create, edit, manipulate, and analyze data or content.
- System Software: Operates in the background and is not directly accessed or controlled by end-users. It manages hardware resources, provides an interface between applications and hardware, and ensures the proper functioning of the computer system.
- Dependency:
- Application Software: Dependent on system software to run. It relies on the underlying operating system and system services provided by the system software to perform tasks and access hardware resources.
- System Software: Independent of application software. It provides the foundational infrastructure and services required for applications to run but does not rely on specific applications.
Q10. What is Object Oriented Language ?
Ans-An object-oriented programming (OOP) language is a programming paradigm that uses objects and classes as fundamental concepts for structuring and organizing software. In an object-oriented language, data and behavior are encapsulated within objects, which are instances of classes.
Block 3 of BCS-11
Q1. What are the features of a browser software ?
Ans-Browser software, also known as web browsers, are applications designed to access and navigate the World Wide Web. They provide users with various features and functionalities to interact with web pages and internet resources. Here are some common features of browser software:
- Graphical User Interface (GUI):
- Browsers typically have a user-friendly graphical interface that allows users to interact with web pages and browser settings using menus, buttons, and other graphical elements.
- Navigation Tools:
- Address Bar: Allows users to enter URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) to navigate to specific websites.
- Back/Forward Buttons: Enable users to navigate backward and forward through previously visited web pages.
- Reload/Refresh Button: Refreshes the current web page to load the latest content.
- Home Button: Returns users to their designated homepage.
- Bookmarks/Favorites: Enable users to save and organize links to their favorite websites for quick access.
- Tabbed Browsing:
- Browsers support tabbed browsing, allowing users to open multiple web pages within the same browser window. Each tab represents a separate web page, making it easier to switch between different websites without opening multiple windows.
- Search Engine Integration:
- Browsers often feature built-in search engine integration, allowing users to perform web searches directly from the browser’s address bar. Users can enter search queries, and the browser will display relevant search results from the selected search engine.
- Security Features:
- HTTPS Support: Browsers support secure HTTPS connections to websites, encrypting data transmitted between the user’s browser and the website to protect against eavesdropping and data tampering.
- Phishing and Malware Protection: Browsers may include features to detect and warn users about potentially harmful websites, phishing attempts, and malicious downloads.
- Privacy Settings: Browsers offer privacy settings and options to control cookies, browsing history, and tracking preferences to enhance user privacy and security.
- Customization Options:
- Themes and Extensions: Browsers allow users to customize the appearance and functionality of the browser through themes and extensions (add-ons or plugins) that add new features or modify existing ones.
- Settings and Preferences: Users can customize browser settings and preferences according to their preferences, such as homepage selection, default search engine, and privacy settings.
- Developer Tools:
- Browsers include built-in developer tools that allow web developers to inspect and debug web pages, analyze network activity, modify HTML/CSS/JavaScript code, and optimize website performance.
- Compatibility and Standards Support:
- Browsers aim to support web standards and ensure compatibility with a wide range of websites and web applications. They regularly update their rendering engines to support new HTML, CSS, and JavaScript features.
Q2. What is E-mail ? Describe it’s advantages and the facilitates it provides. Explain?
Ans-
Email, or electronic mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages over the internet between individuals or groups. It allows users to send and receive messages quickly and efficiently using computers, smartphones, or other internet-enabled devices.
Advantages of email include:
- Speed and Efficiency: Emails can be sent and received almost instantly, facilitating rapid communication between individuals or groups.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional mail, email is significantly cheaper, as it eliminates the need for postage stamps, envelopes, and paper.
- Convenience: Users can access their email accounts from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling communication on the go.
- Asynchronous Communication: Email enables users to send and receive messages at their convenience, without requiring real-time interaction.
- Global Reach: Email transcends geographical boundaries, allowing users to communicate with individuals or groups worldwide.
- Documentation and Archiving: Emails provide a written record of communication, making it easy to track conversations and reference information.
Facilities provided by email include:
- Email Accounts: Users can create email accounts with providers like Gmail, Outlook, or Yahoo, which provide email addresses for sending and receiving messages.
- Inbox: Emails are received and stored in the user’s inbox, where they can be read, replied to, or forwarded.
- Compose: Users can compose new emails by entering the recipient’s email address, subject, and message content. Attachments like files or images can also be included.
- Contacts: Email clients often include a contacts feature for managing contact information, making it easy to address emails to recipients.
- Organization: Emails can be organized into folders or labeled/tagged to categorize and manage messages effectively.
Q3. What is e-Learning ? What are it’s advantages and disadvantages ?
Ans-
e-Learning, or electronic learning, refers to the use of digital technologies and the internet to deliver educational content and facilitate learning experiences remotely. It encompasses a wide range of online learning methods, including online courses, virtual classrooms, multimedia resources, interactive simulations, and digital collaboration tools.
Advantages of e-Learning:
- Accessibility: e-Learning allows learners to access educational content from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling flexible learning schedules and eliminating geographical barriers.
- Convenience: Learners can study at their own pace and on their own schedule, accommodating diverse learning styles and preferences. This flexibility is especially beneficial for working professionals, students with busy schedules, or individuals with mobility limitations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: e-Learning often reduces costs associated with traditional education, such as travel expenses, textbooks, and classroom infrastructure. It can also lower tuition fees for online courses compared to in-person classes.
- Variety of Learning Resources: e-Learning platforms offer a wide range of multimedia resources, including videos, interactive presentations, simulations, and online assessments, enhancing engagement and interactivity.
- Scalability: e-Learning can accommodate large numbers of learners simultaneously, making it suitable for organizations and institutions to scale their training programs or educational offerings without significant infrastructure investments.
Disadvantages of e-Learning:
- Lack of Face-to-Face Interaction: e-Learning may lack the personal interaction and direct communication between instructors and learners found in traditional classroom settings, leading to feelings of isolation or disengagement for some learners.
- Technology Dependence: Successful participation in e-Learning requires access to and proficiency with digital technologies and internet connectivity. Learners who lack access to these resources may face barriers to participation.
- Self-Motivation and Discipline: e-Learning requires self-motivation and discipline to stay on track with coursework and complete assignments independently. Some learners may struggle with time management or procrastination in a self-paced learning environment.
- Quality of Instruction: The quality of e-Learning courses and materials can vary widely depending on the expertise of instructors, instructional design, and production values. Learners may encounter courses that lack depth, interactivity, or effective teaching methodologies.
- Limited Social Interaction: e-Learning may limit opportunities for social interaction and collaboration among learners, which can impact peer learning, networking, and the development of social skills.
Q4. What is data communication ? Explain data communication process with the help of a diagram?
Ans-
Data communication refers to the process of exchanging digital data between two or more devices over a communication medium such as cables, optical fibers, or wireless connections. It involves the transmission, reception, and processing of data to enable communication between devices.
The data communication process typically involves the following components and steps:
- Sender/Transmitter: The sender is the device that originates the data to be transmitted. It converts the data into a format suitable for transmission and initiates the communication process.
- Data: Data refers to the information being transmitted from the sender to the receiver. It can take various forms, including text, images, audio, video, or any other digital content.
- Transmission Medium: The transmission medium is the physical pathway through which data is transmitted between devices. It can be wired (e.g., copper cables, optical fibers) or wireless (e.g., radio waves, microwaves, infrared).
- Receiver: The receiver is the device that receives the transmitted data from the sender. It processes the received data and may perform actions based on the information received.
- Protocols: Protocols are rules and conventions that govern the format, timing, error detection, and error correction mechanisms used in data communication. They ensure reliable and efficient communication between devices.
- Encoding and Decoding: Encoding involves converting the digital data into signals suitable for transmission over the communication medium. Decoding involves converting received signals back into digital data.
Here’s a simplified diagram illustrating the data communication process:
Sender ──(Data)──> Encoding ──(Signals)──> Transmission Medium ──(Signals)──> Decoding ──(Data)──> Receiver
- Sender: The sender originates the data to be transmitted.
- Encoding: The sender encodes the data into signals suitable for transmission over the communication medium.
- Transmission Medium: The signals are transmitted over the transmission medium to the receiver.
- Decoding: The receiver decodes the received signals back into digital data.
- Receiver: The receiver processes the received data and may perform actions based on the information received.
Q5. What is DNS ?
Ans- DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is a decentralized naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the internet or a private network. DNS translates domain names (e.g., www.example.com) into IP addresses (e.g., 192.0.2.1) that computers use to identify each other on the network.
Q6. What is Search Engine ?
Ans-A search engine is a software system designed to search and retrieve information from the vast amount of data available on the internet. Search engines use algorithms to index web pages, documents, images, videos, and other types of content, making them searchable and accessible to users.
Q7. Define the Devices :
- Network Interface Card (NIC): Hardware that enables a computer to connect to a network and communicate with other devices.
- Modem: Device that connects a computer to the internet or a wide area network (WAN) over communication lines like telephone lines or cable lines.
- Hub: Networking device that connects multiple devices in a local area network (LAN), but doesn’t perform intelligent data forwarding like switches.
- Router: Device that connects multiple networks together and forwards data packets between them, determining the best path for each packet.
Q8. What is Guided Media and Unguided Media ?
Ans-Guided Media: Uses physical cables like twisted pair, coaxial, or fiber optic cables to transmit signals.
Unguided Media: Transmits signals wirelessly through the air using technologies like radio waves, microwaves, or infrared waves.
Q9. Characteristics of Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) ?
Ans-Here’s some characteristics of MAN:
- Geographical Coverage: Spans a city or metropolitan area.
- Interconnectivity: Links multiple LANs and locations.
- High Bandwidth: Offers fast data transmission over longer distances.
- Scalability: Can grow to accommodate additional nodes or users.
- Reliability: Engineered for resilience and minimal downtime.
- Service Provisioning: Supports various communication services.
- Cost-Effective: Provides an economical solution for network connectivity.
- Security: Implements measures to protect data and prevent unauthorized access.
Q10. Describe the layers of TCP/IP reference model ?
Ans-The TCP/IP reference model consists of four layers: Application, Transport, Internet, and Link layers.
- Application Layer: Handles network services and applications directly interacting with users, such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS.
- Transport Layer: Facilitates reliable, end-to-end communication between hosts using protocols like TCP and UDP.
- Internet Layer: Responsible for routing and forwarding data packets across different networks using the Internet Protocol (IP).
- Link Layer: Manages data transmission between directly connected devices on the same physical network segment using protocols like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and PPP.
Q11. Explain with the help of a diagram, the 7 layer OSI networking model ?
Ans- The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model comprises seven layers, each with distinct responsibilities:

- Physical Layer: Deals with physical transmission of data, such as cables and connectors.
- Data Link Layer: Ensures error-free data transmission between adjacent nodes and manages access to the physical medium.
- Network Layer: Routes and forwards data packets between different networks based on network addressing.
- Transport Layer: Ensures reliable end-to-end communication between hosts and manages data segmentation and reassembly.
- Session Layer: Manages communication sessions between applications, including establishment and termination.
- Presentation Layer: Handles data representation, encryption, and formatting for exchange between applications.
- Application Layer: Provides network services and interfaces for user applications.
Some Important topics of BCS-11
- LAN and WAN: LAN (Local Area Network) is a network that connects devices within a limited geographical area, like a home, office, or school. WAN (Wide Area Network) is a network that covers a broad area, often connecting LANs across large distances, such as cities or countries.
- Disk Management: Disk management involves organizing, partitioning, formatting, and maintaining storage devices like hard drives or SSDs. It includes tasks such as creating, resizing, and deleting partitions, as well as managing file systems and disk maintenance utilities.
- Memory Management in an Operating System: Memory management in an operating system involves managing computer memory (RAM) efficiently. This includes allocating memory to running programs, optimizing memory usage, and handling memory leaks or errors to ensure smooth system performance.
- Analogue and Digital Signals: Analogue signals are continuous, varying signals that represent information with a continuous waveform. Digital signals are discrete, binary signals that represent information as a series of discrete values (0s and 1s).
- ROM: ROM (Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory that stores firmware or software instructions that are permanently programmed during manufacturing. It retains its contents even when the computer is powered off and is used to store essential system software, such as the BIOS.
- Cookies in the context of Browser Software: Cookies are small pieces of data stored by websites on a user’s computer. They are used to remember user preferences, track user behavior, and provide personalized experiences. Web browsers use cookies to store information such as login credentials, site preferences, and shopping cart items.
- Network Interface Card: A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a hardware component that allows a computer to connect to a network and communicate with other devices. It provides the physical interface for connecting to a network cable (Ethernet) or wireless network (Wi-Fi) and facilitates data transmission between the computer and the network.
- Computer Virus: A computer virus is a type of malicious software (malware) that infects a computer by attaching itself to files or programs and replicating itself. Viruses can cause various harmful effects, such as data loss, system instability, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Characteristics of Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) covers a larger geographical area than a LAN but is smaller than a WAN. Characteristics include high bandwidth, interconnectivity between LANs, scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness for connecting multiple locations within a city or metropolitan area.
- Video Card of a Personal Computer: A video card, also known as a graphics card or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), is a hardware component that renders images and videos on a computer monitor. It accelerates graphics rendering tasks, improves display performance, and supports features like 3D gaming, video editing, and graphics-intensive applications.
- Parallel port and Serial Port: Parallel ports and serial ports are types of physical interfaces used to connect external devices to a computer. Parallel ports transmit data in parallel, sending multiple bits simultaneously, while serial ports transmit data sequentially, one bit at a time. They are used for connecting devices like printers, scanners, and modems.
- SRAM and DRAM: SRAM (Static Random-Access Memory) and DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory) are types of volatile memory used in computers. SRAM is faster and more expensive than DRAM but requires more power and is used for cache memory and high-speed registers. DRAM is slower and less expensive but provides higher storage density and is used for main system memory (RAM).
- Computer Virus: (Already addressed above) A computer virus is a type of malicious software (malware) that infects a computer by attaching itself to files or programs and replicating itself. Viruses can cause various harmful effects, such as data loss, system instability, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Download PDF Of Above Content In 3 Paper
Read More : ECO-01(Business Organisation) Important Short Notes| Expected Question |IGNOU BCA|
Conclusion:
With these IGNOU BCS-011 BCA short notes, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle your exams with confidence. Remember to complement your study efforts with regular practice and mock tests. Good luck!









+ There are no comments
Add yours